IELTS: A Guide to Unlock Global Opportunities


Introduction:
In today’s increasingly interconnected world, proficiency in the English language has become a vital asset for individuals aspiring to pursue international education or seeking migration opportunities. The International English Language Testing System (IELTS) stands as a beacon of language evaluation, facilitating educational and migratory aspirations for millions of non-native English speakers worldwide. This essay explores the significance of IELTS in the context of international education and migration, delving into its purpose, impact, and relevance in shaping the paths of countless individuals.
Background of IELTS:
The IELTS test, developed collaboratively by the British Council, IDP: IELTS Australia, and Cambridge Assessment English, has garnered universal recognition as a benchmark for assessing English language proficiency. Its inception in 1989 was fueled by the growing demand for a standardized measure that could impartially evaluate the language skills of non-native English speakers. As the need for a universally accepted language assessment intensified, IELTS emerged as a reliable instrument that catered to both academic and general purposes.
Purpose of IELTS:
The primary objective of the IELTS test is twofold: to evaluate candidates’ linguistic abilities accurately and to determine their readiness to participate in academic and social settings within English-speaking countries. The test is divided into two main versions: IELTS Academic and IELTS General Training, each designed to cater to specific objectives. The IELTS Academic assesses the language proficiency of students aiming for higher education, while the IELTS General Training targets individuals seeking employment opportunities, training programs, or immigration prospects
The IELTS test plays a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of international education and migration for non-native English speakers. Through its comprehensive evaluation of language skills, IELTS opens doors to academic excellence and better employment prospects, while also acting as a fundamental tool for migration by ensuring effective communication and integration in English-speaking societies.
Importance of IELTS in International Education
IELTS significantly impacts international education, as it serves as a gatekeeper for prospective students vying to embark on academic journeys in English-speaking countries. Universities and academic institutions worldwide rely on IELTS scores to assess the language proficiency of applicants, ensuring they possess the necessary linguistic abilities to thrive in rigorous academic environments.
Role of IELTS in Migration Opportunities
Furthermore, IELTS plays a pivotal role in migration opportunities, acting as a decisive factor for immigration authorities when evaluating the language capabilities of potential immigrants. Many English-speaking countries require IELTS scores as part of visa applications, emphasizing the importance of effective communication in navigating social and professional spheres within their borders.
In the subsequent sections of this essay, we will delve deeper into the positive impacts of IELTS on international education and migration, exploring the benefits it brings to students, professionals, and individuals seeking to establish new lives in foreign lands. Additionally, we will address the challenges and criticisms associated with the test, striving to offer a comprehensive view of IELTS as a powerful tool in shaping global communication and integration.
The IELTS scale is as follows:
- Band Score 9: Expert User – The test-taker has full operational command of the English language. They have a full understanding of complex language, including idiomatic expressions, and can handle both detailed and abstract information.
- Band Score 8: Very Good User – The test-taker has a very good command of the language. They can handle complex language well and understand detailed reasoning. However, occasional errors may still occur.
- Band Score 7: Good User – The test-taker has a good grasp of the language and can understand and use complex language in familiar situations. Some inaccuracies and misunderstandings may occur, especially in unfamiliar contexts.
- Band Score 6: Competent User – The test-taker can understand and communicate effectively in most situations, though there may be some difficulty with complex language and misunderstandings.
- Band Score 5: Modest User – The test-taker has partial command of the language and can handle basic communication in familiar situations, but they may struggle with complex language.
- Band Score 4: Limited User – The test-taker has a basic competence limited to familiar situations. They may have difficulty understanding and expressing themselves in complex language.
- Band Score 3: Extremely Limited User – The test-taker conveys and understands only general meaning in very familiar situations.
- Band Score 2: Intermittent User – The test-taker can understand and communicate only in very basic situations with frequent errors and misunderstandings.
- Band Score 1: Non-User – The test-taker has no ability to use the language, except for a few isolated words.
- Band Score 0: Did not attempt the test – The test-taker did not answer any questions.
Each institution or organization may have specific requirements for the minimum IELTS band score needed for admission, employment, or immigration purposes. It is essential for test-takers to check the specific requirements of their intended institution or destination country to ensure they meet the language proficiency criteria.
Reference:
Required IELTS scores at US universities with Times Higher Education University World Rankings
List Of Minimum IELTS Scores For Canadian Universities 2021 | IDP IELTS
IELTS Test Format
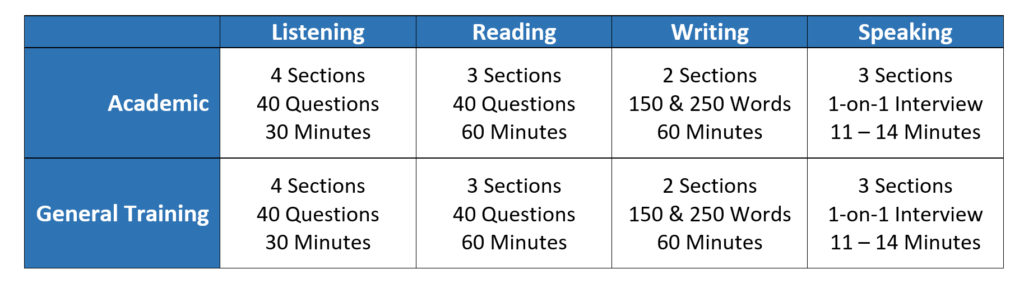
A. Description of the Different IELTS Modules:
- IELTS Academic:
- Explanation of IELTS Academic as the module designed for students applying to study at universities and academic institutions in English-speaking countries.
- Overview of the test’s academic content and tasks that assess a candidate’s readiness for academic studies in English.
- IELTS General Training:
- Introduction to IELTS General Training, which is suitable for individuals planning to migrate to an English-speaking country for work or training purposes.
- Explanation of the test’s emphasis on practical, everyday English language skills needed in social and workplace environments.
B. Overview of the Four Components of the IELTS Test:
- Listening:
- Description of the Listening component, which evaluates a candidate’s ability to understand spoken English in various contexts, such as conversations, monologues, and presentations.
- Explanation of the question types, which may include multiple-choice, matching, and form completion, among others.
- Emphasis on the importance of attentiveness and note-taking during the test.
Reference:
IELTS Listening Recent Actual Tests | IELTS Training Online
- Reading:
- Introduction to the Reading component, which assesses a candidate’s reading comprehension skills through a series of texts, such as articles, advertisements, and extracts from books.
- Explanation of the question types, which might include multiple-choice, True/False/Not Given, and matching headings, among others.
- Tips for effective skimming, scanning, and time management during the reading tasks.
Reference:
IELTS Reading Recent Actual Tests | IELTS Training Online
- Writing:
- Description of the Writing component, which consists of two tasks in both the IELTS Academic and General Training modules.
- Overview of Task 1, where candidates must describe visual information (graphs, charts, diagrams for Academic or a letter for General Training).
- Explanation of Task 2, where candidates must write an essay in response to a prompt on a general topic.
- Guidance on organizing ideas, developing arguments, and managing time during the writing tasks.
Reference:
IELTS Writing Recent Actual Tests 2021 | IELTS Training Online
- Speaking:
- Introduction to the Speaking component, which is a face-to-face interview with an IELTS examiner.
- Explanation of the three parts of the Speaking test: introduction and interview, individual long turn, and discussion.
- Emphasis on the assessment of spoken fluency, coherence, pronunciation, and lexical resource in various conversation topics.
Reference:
IELTS Speaking Recent Actual Tests 2019 | IELTS Training Online
C. Discussion of Test Duration and Timings:
- Overview of the total test duration, which varies depending on the module (IELTS Academic or General Training).
- Explanation of the approximate time allocated for each component (Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking).
- Note on the importance of time management during the test to complete all tasks within the given time limits.
By providing test-takers with this information, Section 2 aims to familiarize candidates with the structure and components of the IELTS test, enabling them to approach the exam with confidence and better preparation.
Reference:
IELTS Test Registration and Preparation
IELTS is widely recognized and conducted in numerous locations worldwide. It is available in more than 1,600 locations across over 140 countries.
To find the nearest IELTS test center and register for the exam, you can visit the official IELTS website or contact the British Council or IDP Education, the two organizations responsible for administering the IELTS test in most countries.
Keep in mind that details and procedures may change over time, so it’s always best to check the official IELTS website or contact the test centers directly for the most up-to-date information on registration and available locations.
Reference: IELTS Registration (britishcouncil.org)
A. Guidance on How to Register for the IELTS Test through the British Council:
- Choose the Test Module: (IELTS Academic or IELTS General Training) based on the candidate’s specific needs and goals.
- Choose where you would like to take the test.
- Decide which format you would like to take the test on. whether on paper or on the computer at the test center.
- Selecting a Test Date and Location: Browse available test dates and locations to choose the most suitable option.
B. Information about Test Dates and Locations:
- Availability of Test Dates: An overview of the IELTS test’s frequency, indicating how often the test is offered throughout the year.
- Test Centers and Locations: Details about the various test centers administered by the British Council, including information on the cities and venues where the IELTS test is conducted.
- Proximity to the Candidate: Advice on selecting a test center that is conveniently located and easily accessible to the candidate.
C. Resources and Support Provided by the British Council for Test Preparation:
- Official IELTS Preparation Materials: Information about the official IELTS preparation materials and resources available through the British Council, such as practice test books, online practice tests, and study guides.
Reference: https://takeielts.britishcouncil.org/take-ielts/prepare/free-ielts-practice-tests
- IELTS Workshops and Seminars: Details about any workshops or seminars organized by the British Council to help candidates better understand the test format, learn effective strategies, and improve their language skills.
- Online Preparation Tools: Introduction to digital learning resources, including interactive exercises, sample questions, and practice tests accessible through the British Council’s online platform.
- Expert Advice and Tips: Highlighting the availability of expert advice from qualified instructors or language professionals who can answer specific questions and provide personalized guidance.
- Mock Test Opportunities: Information on mock tests organized by the British Council to simulate the test-day experience and help candidates gauge their readiness for the actual exam.
- Support for Special Requirements: Explanation of the accommodations and support available for candidates with special requirements, such as those with disabilities or health-related conditions.
By offering detailed guidance on registration, providing information about test dates and locations, and offering a variety of resources and support for test preparation, the British Council aims to ensure that candidates are well-informed, adequately prepared, and confident as they approach the IELTS test. These provisions are designed to help candidates achieve their desired scores and successfully demonstrate their English language proficiency for academic, professional, or migration purposes.
IELTS Test Day Procedures
On the day of your IELTS test, it’s essential to follow certain procedures to ensure a smooth and successful examination experience. Here are the typical IELTS test day procedures:
- Arrival: Arrive at the test center on time, preferably 30 minutes before the scheduled start time. This allows for registration and verification procedures.
- Identification: Bring the same identification document (usually your passport) that you used during the registration process. The ID should be valid and not expired.
- Registration: When you arrive at the test center, you will need to sign in with the test administrators. They will check your identification and registration details.
- Belongings: Most test centers have restrictions on personal belongings in the examination room. Usually, you will be required to store your belongings, including electronic devices, in designated areas.
- Test Room: Once registered, you will be directed to the examination room. In some centers, you might have a designated waiting area before being called into the examination room.
- Seat Allocation: The test administrators will assign you a seat in the examination room.
- Instructions: The test administrator will provide instructions on how the test will be conducted and the rules to follow during the exam.
- Test Format: The IELTS consists of four sections – Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking. The Listening, Reading, and Writing sections are usually conducted in one session, while the Speaking section may be held on the same day or within a few days before or after the other sections.
- Listening and Reading Sections: For the Listening and Reading sections, you will be provided with the necessary materials, such as question booklets and answer sheets.
- Writing Section: In the Writing section, you will need to bring your writing utensils, typically a pen or pencil.
- Speaking Section: If your Speaking test is scheduled on the same day, you will be given a specific time for the Speaking session. This section is often conducted as a face-to-face interview with an examiner.
- Breaks: There are usually no scheduled breaks during the Listening, Reading, and Writing sections. However, there might be short breaks between different sections of the test.
- Follow Instructions: Throughout the test, listen carefully to the instructions provided by the test administrators and follow them accordingly.
- Duration: The overall test duration (including all four sections) is approximately 2 hours and 45 minutes for IELTS Academic and 2 hours and 45 minutes to 3 hours for IELTS General Training.
- Finish: Once the test is completed, you will be allowed to leave the examination room. Remember to collect all your belongings.
Remember, specific procedures may vary slightly depending on the test center, so it’s essential to carefully read any instructions provided by the center and follow them accordingly. Additionally, always bring your official identification and any other required documents to avoid any issues on the test day. Good luck with your IELTS exam!
It’s essential for test-takers to be familiar with the test day procedures to reduce stress and ensure a smooth test-taking experience. By providing detailed explanations about what to expect on the test day, the check-in process, and the rules and regulations in the test room, the British Council aims to create a conducive and fair testing environment for all IELTS candidates. This information also helps candidates understand their responsibilities and what is expected of them to comply with test center guidelines and maintain the integrity of the IELTS test.
IELTS Test Scoring
A. Explanation of the IELTS Band Scale and Scoring System:
The IELTS (International English Language Testing System) test is scored on a 9-band scale, often referred to as the IELTS band score. Each band corresponds to a level of English proficiency, ranging from 1 (non-user) to 9 (expert user). The band scores are used to indicate the test taker’s ability to use English in four language skills: Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking.
The individual band scores for each section are reported in half-band increments (e.g., 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, etc.). There is no overall average of the four sections; each section’s band score is assessed independently.
The process of scoring for each section is as follows:
- Listening: In the Listening section, there are 40 questions, and each question carries one mark. The raw scores (number of correct answers) are then converted to the IELTS 9-band scale using a conversion table.
- Reading: The Reading section also has 40 questions, and the raw scores are converted to the 9-band scale using a conversion table. The difficulty level of the questions in both the Listening and Reading sections can vary between different test versions, but the conversion process ensures fairness in scoring.
- Writing: The Writing section is scored by trained examiners following specific criteria provided by the IELTS. Examiners assess factors such as task achievement, coherence and cohesion, lexical resource (vocabulary), and grammatical range and accuracy. Each criterion is marked on a 9-band scale, and the four criteria are combined to give an overall band score for Writing.
- Speaking: The Speaking section is also assessed by trained examiners using specific criteria. Examiners evaluate the test taker’s fluency, lexical resource, grammatical range and accuracy, and pronunciation. Each criterion is marked on a 9-band scale, and the four criteria are combined to give an overall band score for Speaking.
Once the scores for all four sections have been determined, the average of the four band scores is calculated to obtain the final overall band score. For example, if a test taker receives band scores of 6.5 in Listening, 7.0 in Reading, 6.0 in Writing, and 7.5 in Speaking, the overall band score will be the average of these scores, which is (6.5 + 7.0 + 6.0 + 7.5) / 4 = 6.75, rounded up to the nearest half band, resulting in an overall band score of 7.0.
The IELTS band score provides an accurate reflection of the test taker’s English language proficiency level and is widely recognized by educational institutions, employers, and immigration authorities worldwide.
The IELTS scoring system plays a crucial role in communicating candidates’ English language proficiency to educational institutions, employers, and immigration authorities. By providing a comprehensive explanation of the band scale and scoring system, as well as the process of reporting scores to candidates, the British Council ensures that IELTS test-takers understand how their performance is evaluated and how to interpret the results in the context of their academic or migration goals. The transparency of the scoring process helps candidates gauge their language proficiency accurately and take appropriate steps to improve or use their IELTS scores for their intended purposes
IELTS Test Tips and Strategies
A. General Tips for Each Component of the IELTS Test:
Listening:
- Active Listening: Stay focused and actively listen to the audio recordings. Concentrate on the questions and take notes to catch important details.
- Predict Answers: Anticipate possible answers while listening to the recording to be prepared when the questions are asked.
- Manage Time: Use the 30 seconds provided before each section to read the questions and underline keywords for better comprehension.
- Be Careful with Spelling and Grammar: Pay attention to spelling and grammar as incorrect answers can result from simple mistakes.
Reading:
- Skim and Scan: Quickly skim the text to get a general understanding and scan for specific information when answering questions.
- Focus on Keywords: Identify keywords in the questions and find them in the text to locate relevant information efficiently.
- Be Mindful of Time: Manage time effectively by allocating enough time for each passage and question set.
- Practice Speed Reading: Enhance reading speed and comprehension through regular practice.
Writing:
- Task Response: Address all parts of the writing task and maintain a clear central idea throughout the essay.
- Organize Ideas: Plan the essay structure before writing, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Use Relevant Examples: Support arguments with specific examples and evidence to strengthen your writing.
- Grammar and Vocabulary: Demonstrate a range of grammatical structures and vocabulary to showcase language proficiency.
Speaking:
- Fluency over Accuracy: Focus on speaking fluently and naturally, even if you make minor errors.
- Elaborate on Answers: Provide detailed answers to showcase language skills and expand on ideas.
- Use Paraphrasing: Avoid repetition by using synonyms and paraphrasing in your responses.
- Practice Speaking: Engage in regular speaking practice with friends, teachers, or language partners.
B. Advice on Improving Language Skills and Test-taking Techniques:
- Vocabulary Enhancement: Read extensively to expand your vocabulary and use new words in context. Use vocabulary lists and flashcards for targeted learning.
- Grammar Practice: Regularly practice grammar exercises and seek feedback from teachers or language experts to improve accuracy.
- Listening Practice: Listen to various English audio materials, such as podcasts, news, and movies, to improve your listening comprehension and exposure to different accents.
- Reading Comprehension: Read articles, essays, and books on a wide range of topics to improve reading speed and comprehension.
- Writing Practice: Write essays, reports, and letters regularly to enhance writing skills and develop coherence and cohesion in your writing.
- Speaking Confidence: Engage in conversations with native English speakers or practice speaking in front of a mirror to build confidence in spoken English.
- Mock Tests: Take regular mock tests to simulate the actual test experience and monitor your progress.
- Time Management: Practice time management during practice tests to ensure you can complete all tasks within the allocated time on the actual test day.
By following these tips and strategies, test-takers can improve their language skills, build confidence, and perform better on the IELTS test. Consistent practice and targeted preparation will enable candidates to showcase their English language proficiency effectively and achieve their desired IELTS scores.



